The latest sales figures from the U.S. Mint for August show a significant increase in sales of both gold and silver bullion coins.
The latest sales figures from the U.S. Mint for August show a significant increase in sales of both gold and silver bullion coins.
Sales of gold bullion coins during 2012 have varied dramatically from month to month with a high of 127,000 ounces in January to a low of only 20,000 ounces in April. Monthly gold bullion sales through August have averaged 51,625 ounces.
Monthly sales of silver bullion coins have been more consistent during 2012. The U.S. Mint sold over 6 million ounces of silver bullion coins in January, but the monthly pace has tapered off to under 3 million ounces. The average monthly sales of silver bullion coins through August is 2,817,500.
American Eagle Gold Bullion Coin Sales
Total sales of the American Eagle Gold bullion coins during August totaled 39,000 ounces, up 27.9% from July’s total of 30,500 ounces. Total sales of gold bullion coins by the U.S. Mint through August totaled 413,000 ounces, valued at approximately $700 million based on today’s closing gold price.
On an annualized basis, the U.S. Mint will sell almost 620,000 ounces of gold bullion to investors this year valued at $1.0 billion if the price of gold remains at $1,692. During 2009, the peak year of gold bullion coin sales by the U.S. Mint, investors purchased 1,435,000 ounces valued at $1.4 billion based on the average price of gold of $972 per ounce.
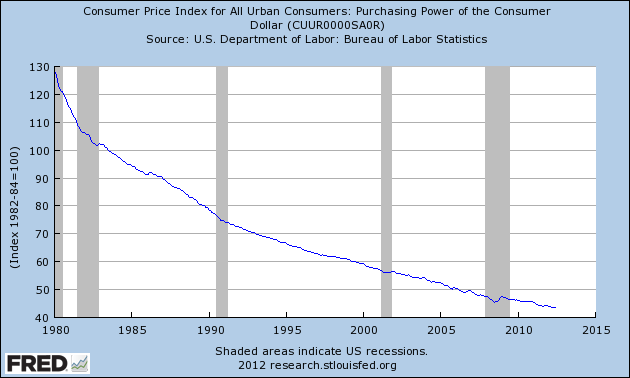
Investors who have reduced gold bullion purchases due to the increased cost per ounce will no doubt regret this decision as the price of gold continues to increase. The value of gold should be viewed in the context of the reduced purchasing power of the dollar – as the Federal Reserve constantly destroys the purchasing power of the U.S. dollar, the “dollar cost” of gold will naturally increase. The price of gold is merely reflecting the fact that paper dollars are worth less and less every day.
As the Fed continues to do what it does, expect the bull market in gold to continue.
Listed below are yearly sales figures for the American Eagle gold bullion coins since 2000. Sales for 2012 are through August 31st.
| Gold Bullion U.S. Mint Sales By Year | ||
| Year | Total Sales Oz. | |
| 2000 | 164,500 | |
| 2001 | 325,000 | |
| 2002 | 315,000 | |
| 2003 | 484,500 | |
| 2004 | 536,000 | |
| 2005 | 449,000 | |
| 2006 | 261,000 | |
| 2007 | 198,500 | |
| 2008 | 860,500 | |
| 2009 | 1,435,000 | |
| 2010 | 1,220,500 | |
| 2011 | 1,000,000 | |
| 2012 | 413,000 | |
| Total | 7,662,500 | |
American Eagle Silver Bullion Coin Sales
Sales of the American Eagle Silver bullion coins by the U.S. Mint during August totaled 2,870,000 ounces, up 25% from the July total of 2,278,000 ounces. Investor demand for silver has remained strong, with many investors taking the opportunity to purchase additional silver below the highs reached during 2011. Sales of the silver bullion coins remain near record levels and total sales for 2012 should be well in excess of 30 million ounces for the third consecutive year.
Total annual sales by the U.S. Mint of the silver bullion coins since 2000 are shown below. Sales for 2012 are through August.
| American Silver Eagle Bullion Coins | ||
| YEAR | OUNCES SOLD | |
| 2000 | 9,133,000 | |
| 2001 | 8,827,500 | |
| 2002 | 10,475,500 | |
| 2003 | 9,153,500 | |
| 2004 | 9,617,000 | |
| 2005 | 8,405,000 | |
| 2006 | 10,021,000 | |
| 2007 | 9,887,000 | |
| 2008 | 19,583,500 | |
| 2009 | 28,766,500 | |
| 2010 | 34,662,500 | |
| 2011 | 39,868,500 | |
| Jul-12 | 22,540,000 | |
| TOTAL | 220,940,500 | |
U.S. Mint Numismatic American Eagle Gold and Silver Coins
Both the American Eagle gold and silver bullion coins can only be purchased from the U.S. Mint by Authorized Purchasers who in turn resell the coins to other dealers and the general public. The numismatic versions of the American Eagle series coins can be purchased directly from the U.S. Mint.
Many of the numismatic silver coins produced by the U.S. Mint attract strong demand and often times, the coins will sell at a premium in the secondary market. A recent example of this is the 2012 San Francisco Silver Eagle Set. According to the Mint News Blog:
The 2012 San Francisco Silver Eagle Set was one of the United States Mint’s most anticipated product releases of the year. Each set contained one 2012-S Proof Silver Eagle and one 2012-S Reverse Proof Silver Eagle.
Product sales began on June 7, 2012 at 12:00 Noon ET with pricing of $149.95 per set. Rather than establishing a maximum product limit, as had been done for similar products in the past, the US Mint would accept orders during a four week ordering window and produce the sets to meet the total demand. A sales odometer which was updated daily gave collectors an indication of the progress of the offering. Sales officially closed on July 5, 2012 at 5:00 PM ET. The last indicated sales total was 251,302 sets.
On the secondary market, prices for the sets remain above the issue price. A quick survey of eBay auctions completed within the past few days show the prices realized for raw sets mostly falling into a range of $180 to $190, compared to the issue price of $149.95.
Sets which have been graded by PCGS or NGC and received the top grade of Proof-70 have sold for premiums above raw sets. Sets with the two coins graded PCGS PR70DCAM and PR70 have recently sold for prices around $425 to $450. Sets with the two coins graded NGC PF 70 Ultra Cameo and PF 70 have sold for prices around $300 to $325.


 By Axel Merk
By Axel Merk
 By Axel Merk
By Axel Merk

 Yahoo Finance ran a story today entitled “Gold, Silver & Copper Are All Heading Lower.” Nothing worth discussing about the specifics of the article – the real story here is that this a classic contrary headline seen at market bottoms, not tops.
Yahoo Finance ran a story today entitled “Gold, Silver & Copper Are All Heading Lower.” Nothing worth discussing about the specifics of the article – the real story here is that this a classic contrary headline seen at market bottoms, not tops. When Ron Paul retires after his current term in Congress, one of the most notable voices for a sound currency and protection of civil liberties against a despotic government will be gone from the official Washington scene. Although Paul was never able to rein in a government that assumes more power over our lives with each passing minute, his warnings gave Americans the opportunity to understand the threats to their financial future and personal liberties.
When Ron Paul retires after his current term in Congress, one of the most notable voices for a sound currency and protection of civil liberties against a despotic government will be gone from the official Washington scene. Although Paul was never able to rein in a government that assumes more power over our lives with each passing minute, his warnings gave Americans the opportunity to understand the threats to their financial future and personal liberties.