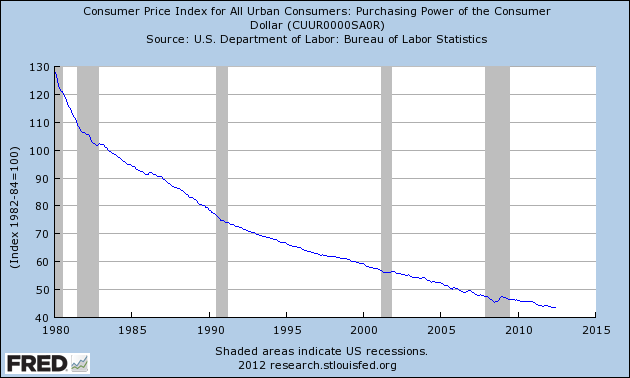
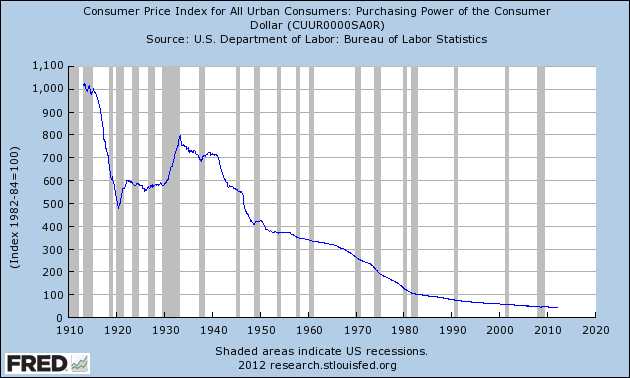
While Wall Street cheers the Federal Reserve’s decision to engage in perpetual quantitative easing, Congressman Ron Paul says the Fed is devastating the U.S. economy through its blatant manipulation of interest rates. According to Ron Paul, manipulating interest rates to the zero bound level has caused a massive misallocation of capital, destroyed the purchasing power of the U.S. dollar and will eventually lead to another financial crisis.
While Wall Street cheers the Federal Reserve’s decision to engage in perpetual quantitative easing, Congressman Ron Paul says the Fed is devastating the U.S. economy through its blatant manipulation of interest rates. According to Ron Paul, manipulating interest rates to the zero bound level has caused a massive misallocation of capital, destroyed the purchasing power of the U.S. dollar and will eventually lead to another financial crisis.
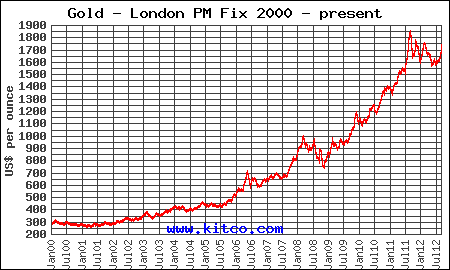
Ron Paul’s warnings have been routinely dismissed by both Wall Street and his colleagues in Congress. The majority of the American public know that something is seriously wrong with our financial system but can’t quite connect the dots between the Fed and lower wages and higher prices. Those who do understand how the Fed is destroying the U.S. economy and are worried about preserving their wealth, should simply copy the investment strategy of Ron Paul who has gone all in on gold and silver.
One of the most enduring myths in the United States is that this country has a free market, when in reality, the market is merely the structural shell of formerly free institutions. Government pulls the strings behind the scenes. No better illustration of this can be found than in the Federal Reserve’s manipulation of interest rates.
The Fed has interfered with the proper function of interest rates for decades, but perhaps never as boldly as it has in the past few years through its policies of quantitative easing. In Chairman Bernanke’s most recent press conference he stated that the Fed wishes not only to drive down rates on Treasury debt, but also rates on mortgages, corporate bonds, and other important interest rates. Markets greeted this statement enthusiastically, as this means trillions more newly-created dollars flowing directly to Wall Street.
Because the interest rate is the price of money, manipulation of interest rates has the same effect in the market for loanable funds as price controls have in markets for goods and services. Since demand for funds has increased, but the supply is not being increased, the only way to match the shortfall is to continue to create new credit. But this process cannot continue indefinitely. At some point the capital projects funded by the new credit are completed. Houses must be sold, mines must begin to produce ore, factories must begin to operate and produce consumer goods.
But because consumption patterns have either remained unchanged or have become more present-oriented, by the time these new capital projects are finished and begin to produce, the producers find no market for their goods. Because the coordination between savings and consumption was severed through the artificial lowering of the interest rate, both savers and borrowers have been signaled into unsustainable patterns of economic activity. Resources that would have been used in productive endeavors under a regime of market-determined interest rates are instead shuttled into endeavors that only after the fact are determined to be unprofitable. In order to return to a functioning economy, those resources which have been malinvested need to be liquidated and shifted into sectors in which they can be put to productive use.
Another effect of the injections of credit into the system is that prices rise. More money chasing the same amount of goods results in a rise in prices. Wall Street and the banking system gain the use of the new credit before prices rise. Main Street, however, sees the prices rise before they are able to take advantage of the newly-created credit. The purchasing power of the dollar is eroded and the standard of living of the American people drops.
We live today not in a free market economic system but in a “mixed economy”, marked by an uneasy mixture of corporatism; vestiges of free market capitalism; and outright central planning in some sectors. Each infusion of credit by the Fed distorts the structure of the economy, damages the important role that interest rates play in the market, and erodes the purchasing power of the dollar. Fed policymakers view themselves as wise gurus managing the economy, yet every action they take results in economic distortion and devastation.
Unless Congress gets serious about reining in the Federal Reserve and putting an end to its manipulation, the economic distortions the Fed has caused will not be liquidated; they will become more entrenched, keeping true economic recovery out of our grasp and sowing the seeds for future crisis.
 After what appeared to be a coordinated effort by Europe and the U.S. to print their way to prosperity, Japan quickly joined the race to eternal QE with the
After what appeared to be a coordinated effort by Europe and the U.S. to print their way to prosperity, Japan quickly joined the race to eternal QE with the 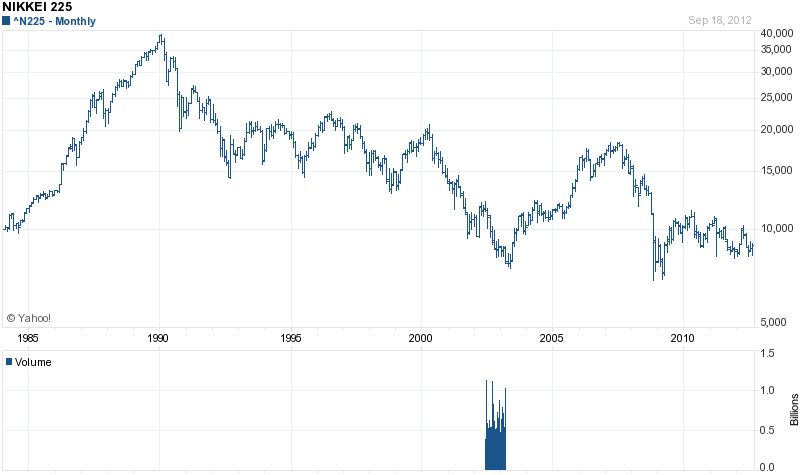

 By Axel Merk
By Axel Merk By
By 

 Legendary bond king investor Bill Gross, who presides over the world’s largest bond funds makes a compelling case for owning gold in an interview with Bloomberg TV. Lead manager of influential Pacific Investment Management Company (PIMCO) since 1987, Bill Gross reputedly made $200 million in 2011.
Legendary bond king investor Bill Gross, who presides over the world’s largest bond funds makes a compelling case for owning gold in an interview with Bloomberg TV. Lead manager of influential Pacific Investment Management Company (PIMCO) since 1987, Bill Gross reputedly made $200 million in 2011. Benjamin Franklin, one of the most eloquent wordsmiths in American history, coined one of the most famous quotations of all time in a letter to Jean-Baptiste Leroy in 1789.
Benjamin Franklin, one of the most eloquent wordsmiths in American history, coined one of the most famous quotations of all time in a letter to Jean-Baptiste Leroy in 1789. India may increase the import tax on gold for the third time this year in an attempt to shore up the weak rupee. Purchases of gold and silver account for a huge 12.5% of all Indian imports and are contributing to a record current-account deficit according to
India may increase the import tax on gold for the third time this year in an attempt to shore up the weak rupee. Purchases of gold and silver account for a huge 12.5% of all Indian imports and are contributing to a record current-account deficit according to 

 In August Ron Paul accused the U.S. Treasury “
In August Ron Paul accused the U.S. Treasury “