Both the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan have gone all in with their attempts to revive weak, debt burdened economies with a pledge of unlimited money printing.
Both the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan have gone all in with their attempts to revive weak, debt burdened economies with a pledge of unlimited money printing.
Japan’s incoming Liberal Democratic Party Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, who ran on a platform of unlimited quantitative easing and higher inflation, has quickly forced capitulation by the Bank of Japan to surrender its independence from political influence.
The Bank of Japan pledged Thursday to review its price stability goal, admitting that the move was partly in response to incoming Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s aggressive calls for the central bank to step up its fight against deflation.
At its two-day policy board meeting, the BOJ decided to expand the size of its asset-purchase program—the main tool of monetary easing with interest rates near zero—and promised to review next month its current inflation goal, something Mr. Abe demanded during Japan’s parliamentary campaign.
Countering speculation that the board’s decision-making process is being driven by politicians, Gov. Masaaki Shirakawa said the bank reviews its price goal every year. But he acknowledged that the policy board had taken Mr. Abe’s request into account.
The Bank of Japan’s quick surrender of monetary policy independence reflected the fact that they had little choice in the matter. Mr. Abe had previously threatened a “law revision to take away the BOJ’s independence if it didn’t comply with his demands. Mr. Abe said the election shows that his views have the support of the people, and, on the night of his victory, he specifically said he expected the BOJ to do something at this week’s meeting.”
The policy of unlimited money printing by Japan came shortly after similar actions were announced by the U.S. Federal Reserve in early December. Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke, architect of the U.S. “economic recovery” announced that the Fed would purchase $45 billion of US Treasuries every month in addition to the open ended monthly purchase of $40 billion of mortgage backed securities. The Fed’s expanded “asset purchase programs” will be monetizing over $1 trillion of assets annually, effectively funding a large portion of the U.S. government’s annual deficit with printed money.
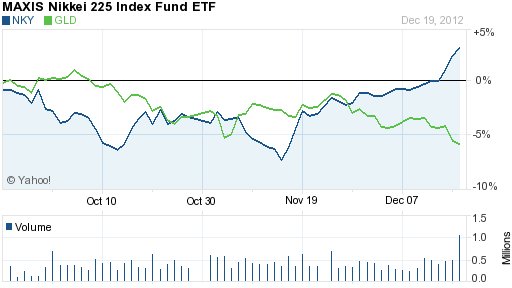
The impact of blatantly unlimited money printing by two of the world’s largest economies surprised many gold investors as the price of stocks and gold quickly diverged, with gold selling off and stocks (especially in Japan) gaining.
Why would gold, the only currency with intrinsic value that cannot be debased by governments, sell off as governments pledged to flood the world with freshly printed paper currencies? Here’s one insight from John Mauldin.
When you reduce the amount of leverage in the system, you’re actually reducing the total money supply. So the Fed can come in and print money, and the money supply – the total amount of credit and leverage and material that’s going through the system – really hasn’t increased.
A lot of monetary economic theories say “the money supply is directly related to inflation.”
It is, but the amount of leverage and credit in the system is also directly related to inflation. It becomes a much more complicated mix. What happens at the end of the debt supercycle, as you’re reducing that leverage, you’re actually in a deflationary world. That is the whole debate between deflation and inflation.
If you read the polls in the United States, we’re just totally dysfunctional. We want to pay less taxes and we want more health care – that doesn’t work. We are going to have to be adults and recognize that problem.
The reason is the Fed is going to do everything they can to fight deflation. The only thing they can do is to print money. They’re going to be able to print more money than any of us can possibly imagine and get away with it without having inflation.
Mr. Mauldin may have a valid point, but a more likely explanation is the suppression of gold prices by governments and central banks as voluminously documented by GATA.
“Those who follow GATA may not be surprised when the monetary metals markets don’t make sense, since they really aren’t markets at all but the targets of constant intervention by governments.”

 By
By 
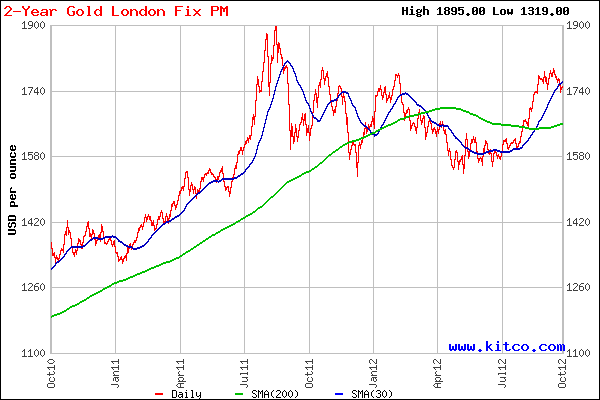
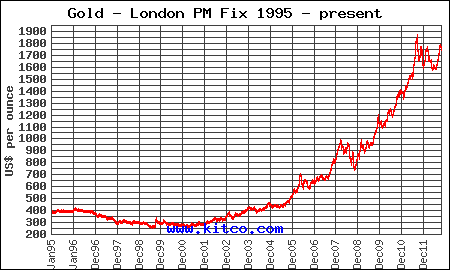
 Gold has had a volatile year. From January’s opening price of $1,598, gold quickly moved up by $183 per ounce by the end of February. An ensuing correction that lasted into July brought the price of gold down by $225 per ounce to $1,556 in mid July, the low of the year. In August gold started to rally, closing yesterday at $1716.25 per ounce, up $118.25 or 7.4% on the year.
Gold has had a volatile year. From January’s opening price of $1,598, gold quickly moved up by $183 per ounce by the end of February. An ensuing correction that lasted into July brought the price of gold down by $225 per ounce to $1,556 in mid July, the low of the year. In August gold started to rally, closing yesterday at $1716.25 per ounce, up $118.25 or 7.4% on the year.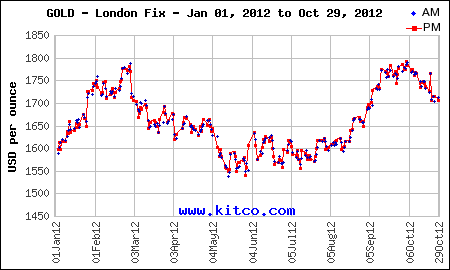
 By
By 
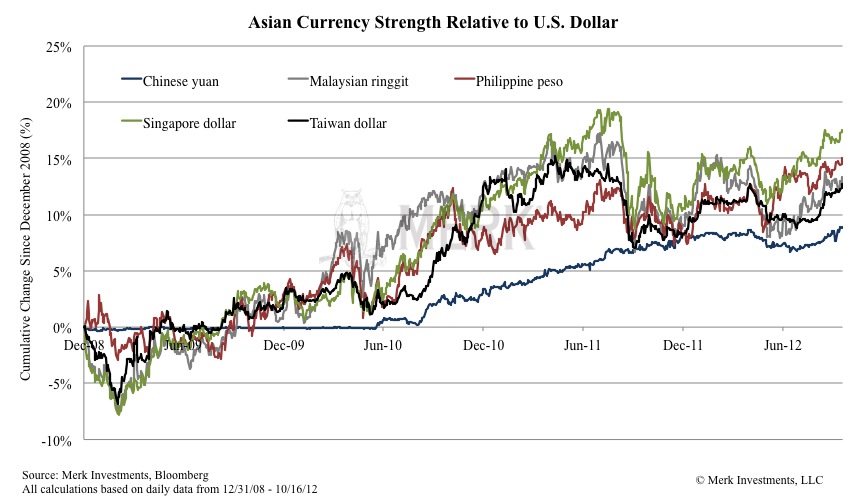

 By
By 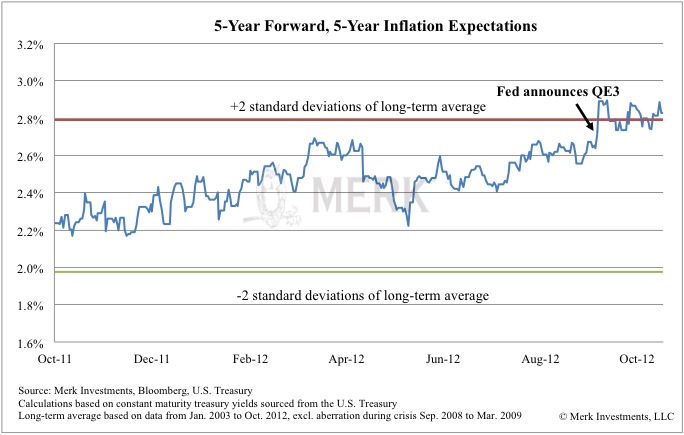




 By Axel Merk & Yuan Fang
By Axel Merk & Yuan Fang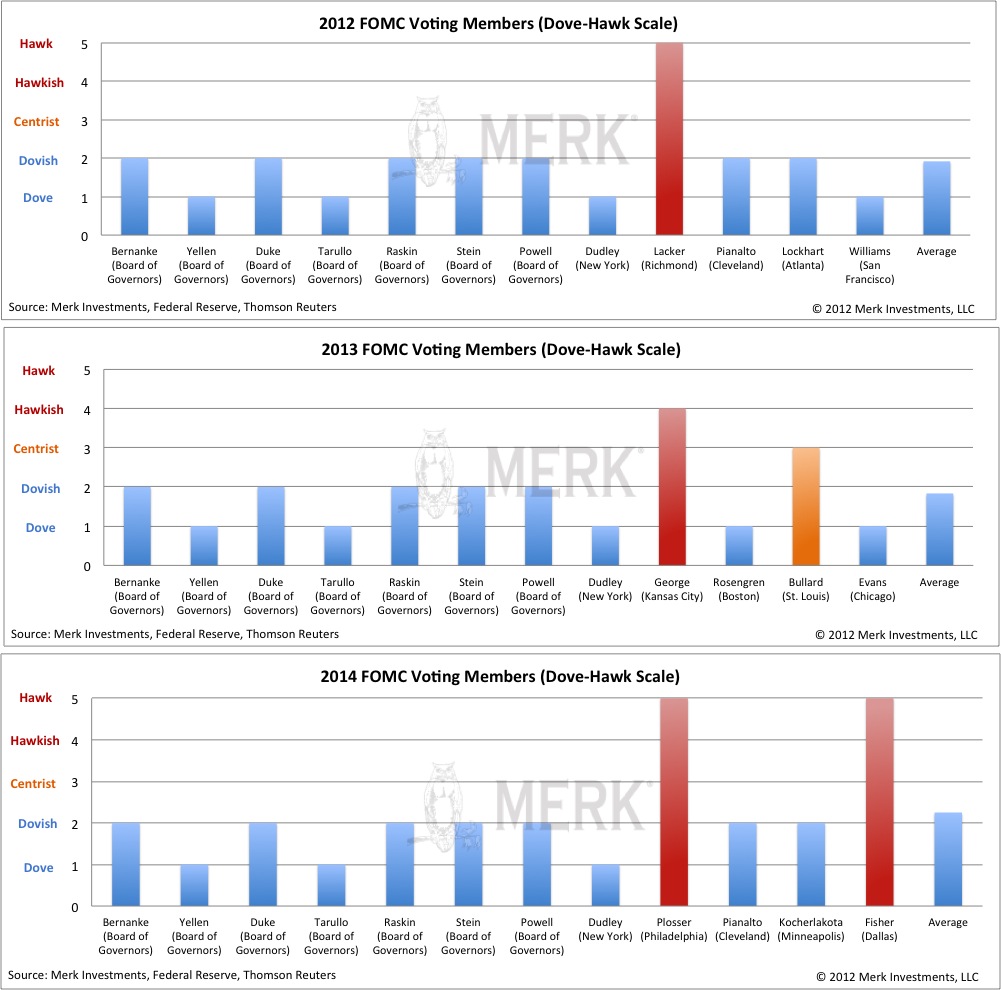
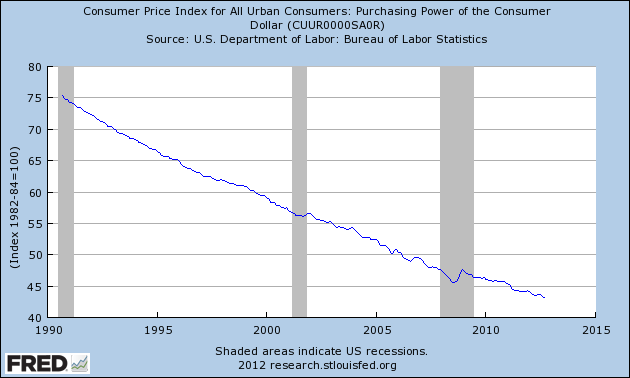
 In an effort to expand credit and spur job creation, the Federal Reserve has massively expanded its balance sheet with the most aggressive monetary policies in the history of the Federal Reserve. Since the start of the financial crisis, the Fed instituted two rounds of quantitative easing under which over $2.75 trillion of debt securities were purchased by, in effect, printing money.
In an effort to expand credit and spur job creation, the Federal Reserve has massively expanded its balance sheet with the most aggressive monetary policies in the history of the Federal Reserve. Since the start of the financial crisis, the Fed instituted two rounds of quantitative easing under which over $2.75 trillion of debt securities were purchased by, in effect, printing money.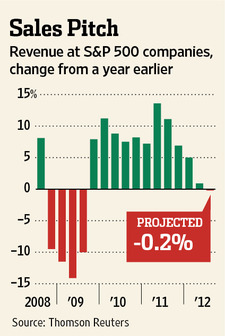
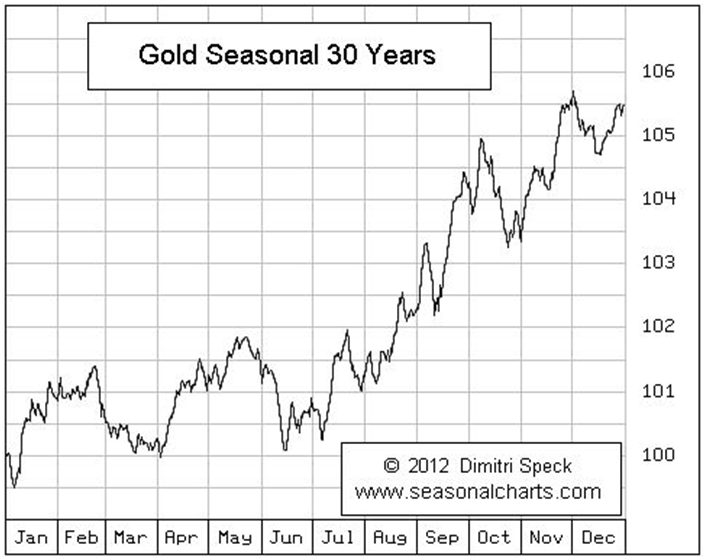
 The third quarter 2012 Investment Statistics Commentary released today by the World Gold Council summarizes the performance of gold in various currencies and explores reasons why demand for gold should continue to increase.
The third quarter 2012 Investment Statistics Commentary released today by the World Gold Council summarizes the performance of gold in various currencies and explores reasons why demand for gold should continue to increase.