By Axel Merk
By Axel Merk
Doubling down on QE3, the Federal Reserve (Fed) Chairman Bernanke tells China and Brazil: allow your currencies to appreciate. One does not need to be a rocket scientist to conclude that Bernanke wants the U.S. dollar to fall. Is it merely a war of words, or an actual war? Who is winning the war?
The cheapest Fed policy is one where a Fed official utters a few words and the markets move. Rate cuts are more expensive; even more so are emergency rate cuts and the printing of billions, then trillions of dollars. As such, the Fed’s communication strategy may be considered part of a war of words. Indeed, the commitment to keep interest rates low through mid 2015 may be part of that category. But quantitative easing goes beyond words: QE3, as it was announced last month, is the Fed’s third round of quantitative easing, a program in which the Fed is engaging in an open-ended program to purchase Mortgage Backed Securities (MBS). To pay for such purchases, money is created through the strokes of a keyboard: the Fed credits banks with “cash” in payment for MBS, replacing MBS on bank balance sheets with Fed checking accounts. Through the rules of fractional reserve banking, this cash can be multiplied on to create new loans and expand the broader money supply. The money used for the QE purchases is created out of thin air, not literally printed, although even Bernanke has referred to this process as printing money to illustrate the mechanics.
Why call it a war? It was Brazil’s finance minister Guido Mantega that first coined the term, accusing Bernanke of starting a currency war. Here’s the issue: like any other asset, currencies are valued based on supply and demand. When money is printed, all else equal, supply increases, causing a currency to decline in value. In real life, the only constant is change, allowing policy makers to come up with complex explanations as to why printing money does not equate to debasing a currency. But even if intentions may have a different primary focus, our assessment is that a central bank that engages in quantitative easing wants to weaken its currency. It becomes a war because someone’s weak currency is someone else’s strong currency, with the “winner” being the country with the weaker currency. The logic being a weaker currency promotes net exports and GDP growth. If the dollar is debased through expansionary monetary policy, there is upward pressure on other currencies. Those other countries like to export to the U.S. and feel squeezed by U.S. monetary policy. Given that politicians the world over never like to blame themselves for any shortcomings, the focus of international policy makers quickly becomes the Fed’s monetary largesse.
Bernanke speaking at an IMF sponsored seminar in Tokyo pointed to the other side of the coin: if China, Brazil and others don’t like his policies because they create inflation back home, they should allow their currencies to appreciate. But these countries are reluctant as stronger currencies lead to a tougher export environment.
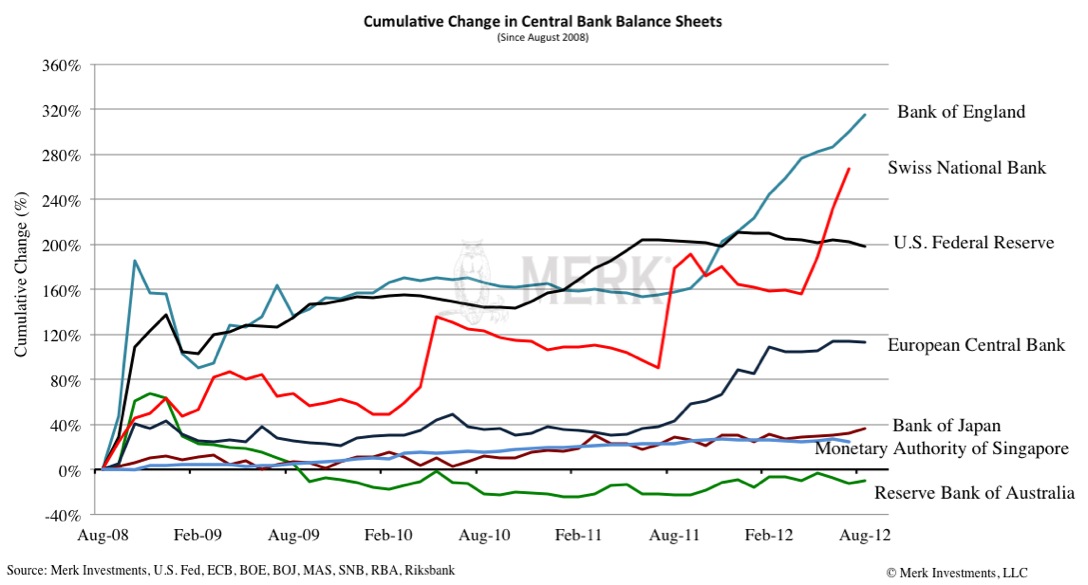
Now keep in mind that it is always easier to debase a currency than to strengthen it. Switzerland, the previously perceived safe haven by many investors, has taken the lead. Using a central bank’s balance sheet as a proxy for the amount of money that has been printed, the Swiss National Bank’s printing press has surpassed that of the Federal Reserve considering relative growth since August 2008. Again note that no real money has been directly printed in these programs; also note that some activities, such as the sterilization of bond purchases by the European Central Bank, cause a central bank balance sheet to grow, even if sterilization reflects a “mopping up” of liquidity:
Japan has warned about intervening in the markets on multiple occasions, but the size of the Japanese economy as well as the lack of political will make an intentional debasement more difficult. Indeed, the Japanese did their money printing in the 1990s, but forgot we had a financial crisis in recent years.
Bernanke does acknowledge the concerns of emerging markets, but argues they are blown out of proportion. He elaborates that undervaluation and unwanted capital inflows are linked: allow your currencies to appreciate (versus the dollar) and you won’t have to be afraid of excessive capital inflows, inflation and asset bubbles. Ultimately, and importantly, Bernanke says the Fed will continue its course, suggesting that it will strengthen the U.S. economic recovery; and by extension, strengthen the global economy.
Let’s look at the issue from the viewpoint of emerging markets: policy makers like to promote economic growth, among other methods, through a cheap exchange rate, up to a certain point. They don’t want too much inflation or too many side effects. Historically, they manage these side effects with administrative tools. However, taking China as an example, taming price pressure through, say, price controls, has not been very effective. We believe that’s a good thing, as China would otherwise experience product shortages akin to what the Soviet Union experienced. Conversely, however, China must employ a broader policy brush to contain inflationary pressures. We believe – and Bernanke appears to agree – currency appreciation is one of the more effective tools.
So how will this currency war unfold? The ultimate winner may well be gold. But as the chart above shows, it’s not simply a race to the bottom. If one considers what type of economy can stomach a stronger currency, our analysis shows an economy competing on value rather than price has more pricing power and therefore the greater ability to handle it. Vietnam mostly competes on price; as such, the country has, more than once, engaged in competitive devaluation. At the other end of the spectrum in emerging markets may be China: having allowed its low-end industries to move to lower cost countries, China increasingly competes on value. Within Asia, we believe the more advanced economies have the best potential to allow their currencies to appreciate. It’s not surprising to us that China’s Renminbi just recently reached a 19-year high versus the dollar.
What we have little sympathy for is an advanced economy, e.g. the U.S., competing on price. We very much doubt the day will come when we export sneakers to Vietnam. As such, a weak dollar only provides the illusion of strength with exports temporarily boosted. Yet the potential side effects, from inflation to the sale of assets to foreign investors with strong currencies, may not be worth the risk.
Please register to join us as we discuss winners and losers of the unfolding currency wars in our Webinar this Thursday, October 18, 2012.
Axel Merk is President and Chief Investment Officer, Merk Investments
Merk Investments, Manager of the Merk Funds.
 By Axel Merk
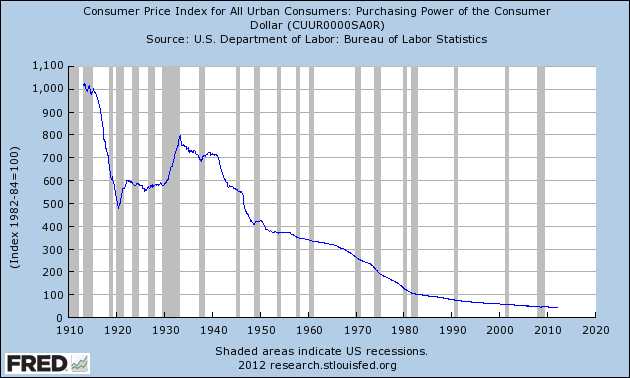
By Axel Merk While Wall Street cheers the Federal Reserve’s decision to engage in perpetual quantitative easing, Congressman Ron Paul says the Fed is devastating the U.S. economy through its blatant manipulation of interest rates. According to Ron Paul, manipulating interest rates to the zero bound level has caused a massive misallocation of capital, destroyed the purchasing power of the U.S. dollar and will eventually lead to another financial crisis.
While Wall Street cheers the Federal Reserve’s decision to engage in perpetual quantitative easing, Congressman Ron Paul says the Fed is devastating the U.S. economy through its blatant manipulation of interest rates. According to Ron Paul, manipulating interest rates to the zero bound level has caused a massive misallocation of capital, destroyed the purchasing power of the U.S. dollar and will eventually lead to another financial crisis.
 By Axel Merk
By Axel Merk By
By 

 Benjamin Franklin, one of the most eloquent wordsmiths in American history, coined one of the most famous quotations of all time in a letter to Jean-Baptiste Leroy in 1789.
Benjamin Franklin, one of the most eloquent wordsmiths in American history, coined one of the most famous quotations of all time in a letter to Jean-Baptiste Leroy in 1789. In August Ron Paul accused the U.S. Treasury “
In August Ron Paul accused the U.S. Treasury “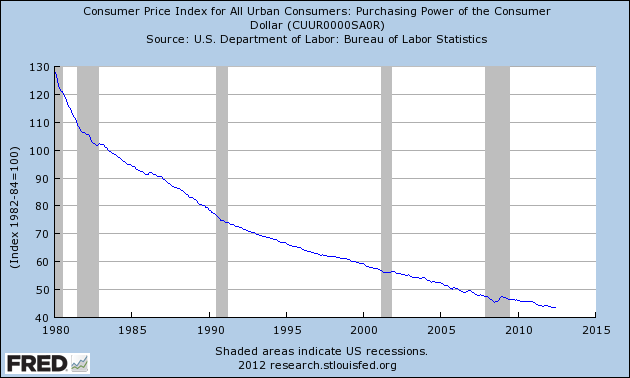
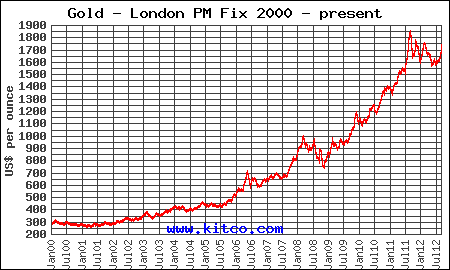
 The latest sales figures from the U.S. Mint for August show a significant increase in sales of both gold and silver bullion coins.
The latest sales figures from the U.S. Mint for August show a significant increase in sales of both gold and silver bullion coins.

 By Axel Merk
By Axel Merk