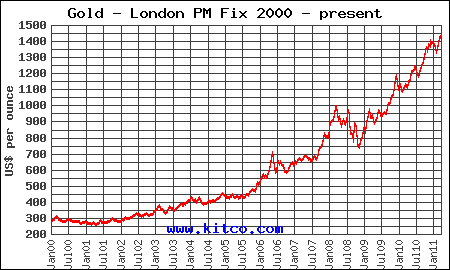
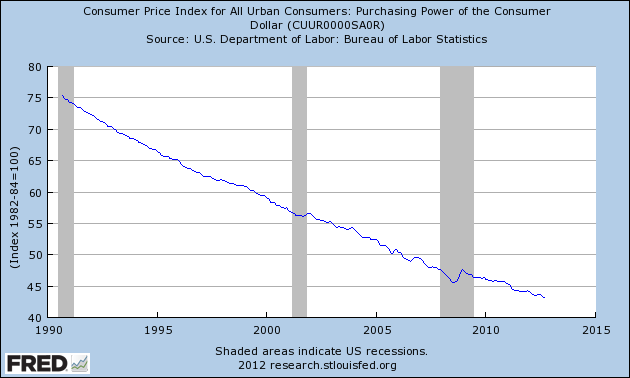
Americans need to take a serious look at how the purchasing power of the dollar is being destroyed. Rampant poverty, declining real incomes and higher prices are all the guaranteed results of a Federal Reserve that remains committed to destroying the value of the dollar. A dollar saved today that has less purchasing power a year from now equates to the “silent” destruction of the dollar, an event which has gone virtually unnoticed and unprotested by the American public.
Americans need to take a serious look at how the purchasing power of the dollar is being destroyed. Rampant poverty, declining real incomes and higher prices are all the guaranteed results of a Federal Reserve that remains committed to destroying the value of the dollar. A dollar saved today that has less purchasing power a year from now equates to the “silent” destruction of the dollar, an event which has gone virtually unnoticed and unprotested by the American public.
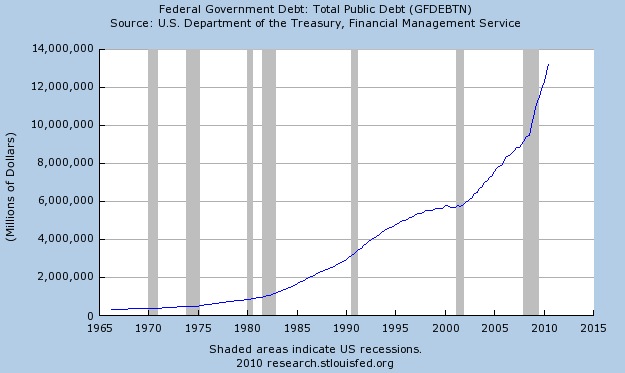
Act #4 of the Fed’s endless money printing campaign directly monetizes over a half a trillion dollars of U.S. deficit spending annually. In addition to financing the Federal debt with printed dollars, the Fed has also explicitly endorsed an inflation rate of 2.5% as being “acceptable.”
Even a relatively “benign” inflation rate of 2.5% rapidly erodes the purchasing power of savings. Over a short 5 years, the purchasing power of $100,000 in savings is reduced to $88,110 at an inflation rate of 2.5%. At a 5% inflation rate, the value after 5 years is only $77,378. We don’t even want to look at how much purchasing power would be lost over a decade.
Both consumers and especially savers need to become aware of the wealth depletion caused by purchasing power loss. From my experience, most people find it conceptually difficult to see a real loss (in purchasing power) when there has been no change in the principal amount of savings. As John Maynard Keynes wrote in 1920, “By a continuing process of inflation, governments can confiscate, secretly and unobserved, an important part of the wealth of their citizens. By this method they not only confiscate, but they confiscate arbitrarily; and while the process impoverishes many, it actually enriches some. And not one man in a million will detect the theft.”
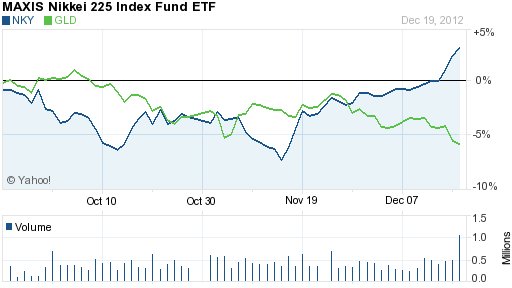
Incredibly, the desperate attempts of central banks to prop up the over-indebted financial system via inflation and money printing is viewed as beneficial by some misguided economists. Japan’s decision to go all in with “unlimited quantitative easing” was applauded in a recent Slate commentary.
That’s because Shinzo Abe, the overwhelming favorite to lead the Liberal Democratic Party to victory, is running on a bold platform of unlimited quantitative easing and more inflation. If this works—and the odds are that it will—Abe will not only cure a great deal of what ails Japan, he’ll light a path forward for the rest of the developed world.
But if he (Abe) does manage to stick to his guns, the odds are good that it will work. Monetary expansion should reduce the price of the yen and goose exports. More importantly, it will push domestic real interest rates down and spur investment. Creating firm expectations that yen-denominated prices will be higher in the future than they are today should encourage firms and households alike to acquire real goods sooner rather than later. And all this ought to encourage everyone to be investing and spending more.
Bernanke said Japan’s central bankers needed Rooseveltian resolve, but the moral of the story may be that it takes a politician—a Roosevelt—to have the clout and legitimacy to make central banks act decisively when an economy gets firmly mired at the lower bound. If Abe can be that Roosevelt, he’ll not only be a hero of Japan but possibly of the whole world economy. After all, if America’s old advice to Japan turns out to work in practice as well as in theory, then maybe we’ll finally get around to taking our own advice for ourselves.
Does anyone think that Japan’s temporary benefit of a lower currency will not be met with competitive devaluations by other nations? Exactly how will Japanese consumers be able to spend more if prices increase and wages remain stagnant due to the limiting effects of wage globalization? The Slate author firmly espouses the lunacy of currency debasement as a wealth enabler despite the fact that no nation in history has ever printed its way to prosperity.
The fact that central banks have firmly committed themselves to money printing on an unimaginable scale is not a cause for hope but rather a clear signal of desperation. Policy makers have run out of options and in an attempt to forestall the collapse of the financial system, have turned to the last resort option of unlimited money printing.
 Both the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan have gone all in with their attempts to revive weak, debt burdened economies with a pledge of unlimited money printing.
Both the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan have gone all in with their attempts to revive weak, debt burdened economies with a pledge of unlimited money printing.