The Perth Mint presents a neat infographic on the world’s top 10 gold producing countries.
The Perth Mint presents a neat infographic on the world’s top 10 gold producing countries.
China, which loves gold more than anything, came in as the number one producer with annual output of 370 metric tons. According to the latest official numbers from the IMF, China holds the world’s fifth largest reserves of gold with holdings of 33.9 million ounces. Unofficially, many analysts say that actual gold reserves held by China are far larger than the “officially” reported numbers.
The second largest gold producer in the world is Australia (home of the Perth Mint) which produced 250 metric tons of gold in 2012.
The United States came in at third place with annual production of 230 metric tons. As a dubious consolation for those who hate to see the U.S. come in third, keep in mind that the United States still reigns supreme in the number one spot for production of paper currency.
The Perth Mint, which has been producing gold coins since 1899 has produced (in my opinion) some of the world’s most artistic gold and silver coins.
 In an interview with CNBC, former GOP presidential candidate Ron Paul endorsed the efforts of his son, Senator Rand Paul, to hold up the nomination of Janet Yellen as Federal Reserve Chairman until laws are passed requiring more transparency from the Fed.
In an interview with CNBC, former GOP presidential candidate Ron Paul endorsed the efforts of his son, Senator Rand Paul, to hold up the nomination of Janet Yellen as Federal Reserve Chairman until laws are passed requiring more transparency from the Fed.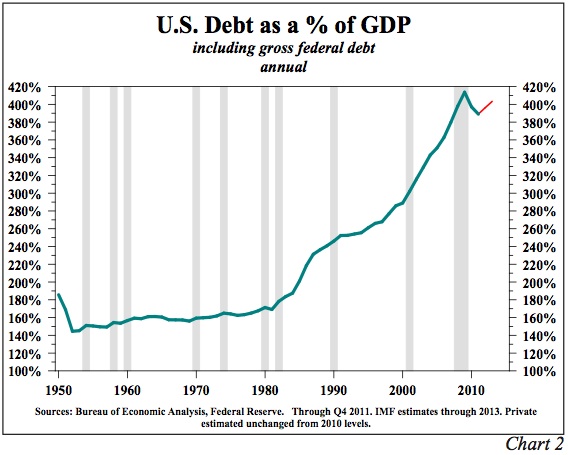
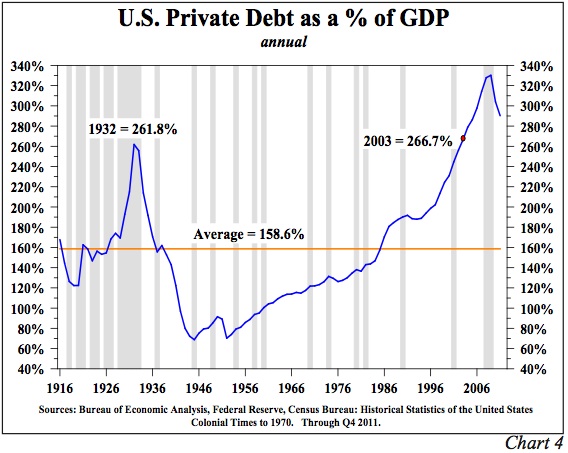
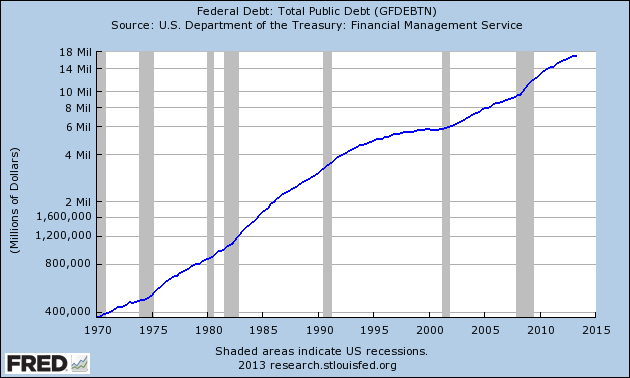
 Gold has been on a rampage since the early 2000’s with yearly gains for 12 years in a row. Nothing lasts forever and the number 13 is starting to look very unlucky for gold. Barring a major upset in the world financial system, it looks increasing likely that gold will decline in the 13th year of its long rally in the year 2013.
Gold has been on a rampage since the early 2000’s with yearly gains for 12 years in a row. Nothing lasts forever and the number 13 is starting to look very unlucky for gold. Barring a major upset in the world financial system, it looks increasing likely that gold will decline in the 13th year of its long rally in the year 2013.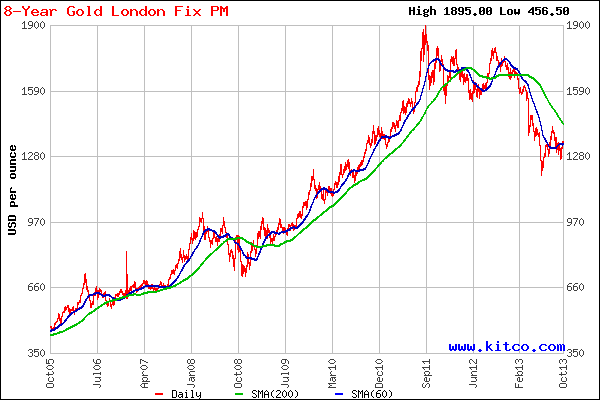
 In an
In an 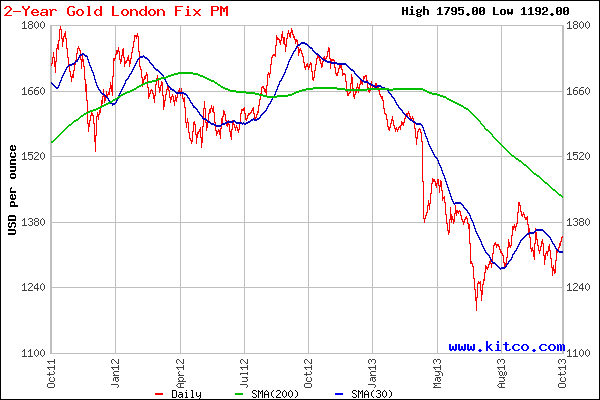
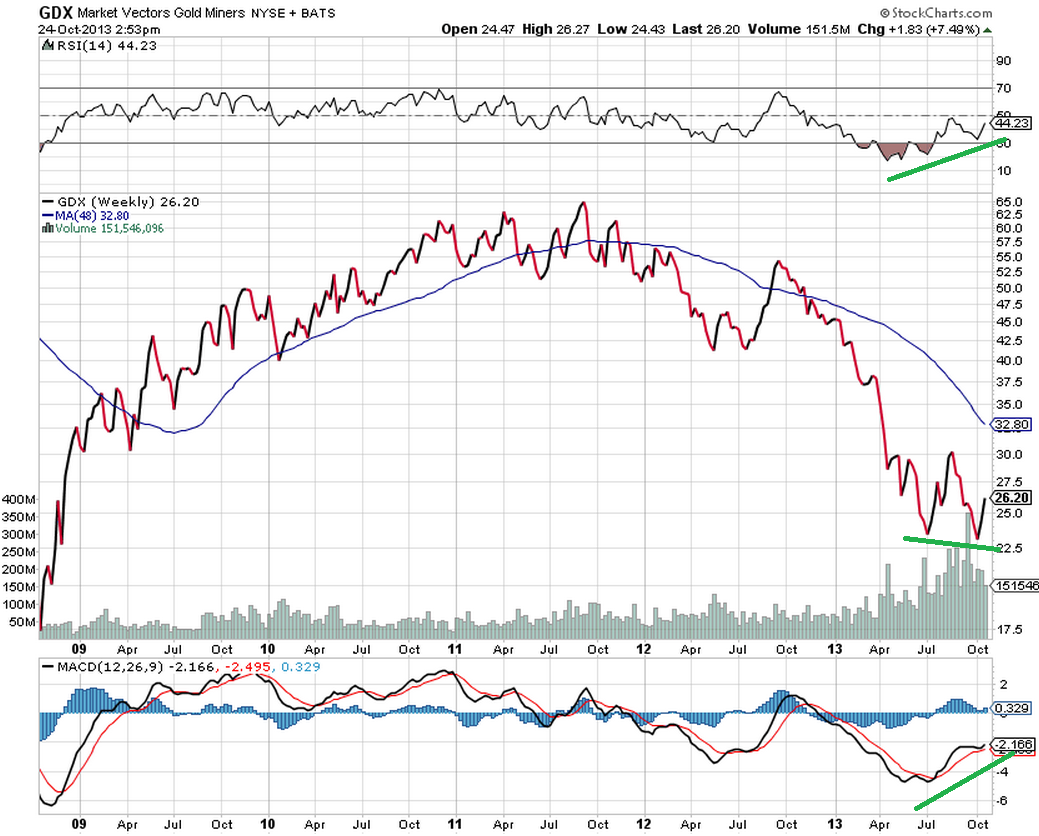
 The bear case for gold and silver stocks is well known and investors have reacted by dumping mining stocks indiscriminately. The staggering decline in gold and silver stocks over the past two years now exceeds the decline that occurred during the crash of 2008 when the financial system was at the brink of collapse.
The bear case for gold and silver stocks is well known and investors have reacted by dumping mining stocks indiscriminately. The staggering decline in gold and silver stocks over the past two years now exceeds the decline that occurred during the crash of 2008 when the financial system was at the brink of collapse.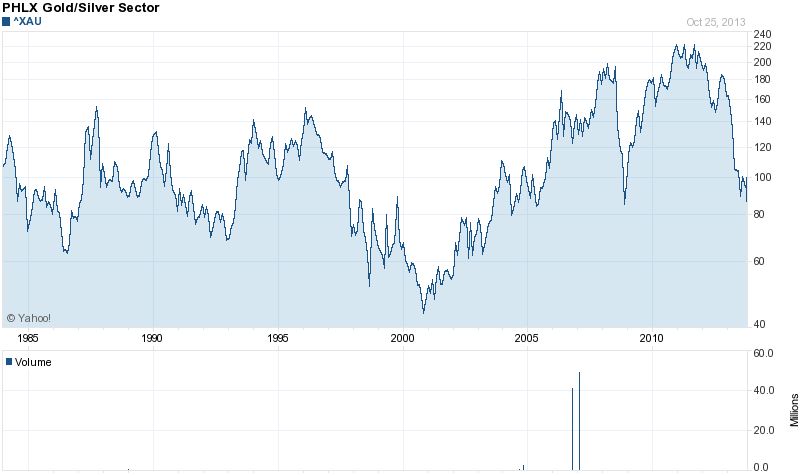
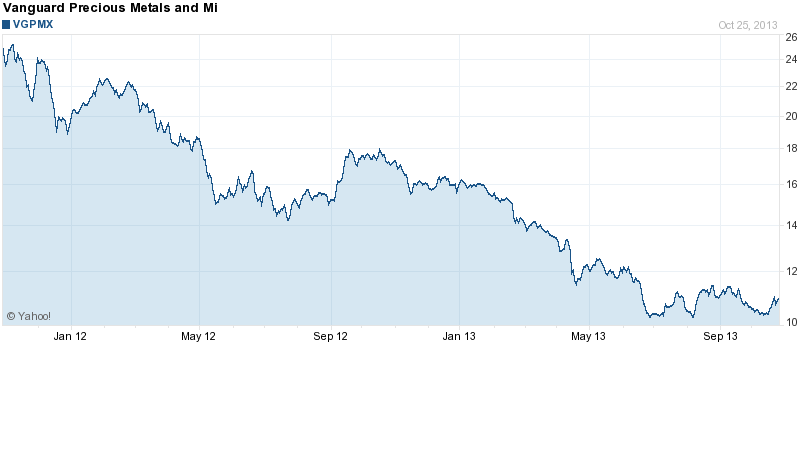
 By: GE Christenson
By: GE Christenson



 Demand for American Eagle gold and silver bullion coins remained sluggish in September according to the latest figures from the U.S. Mint.
Demand for American Eagle gold and silver bullion coins remained sluggish in September according to the latest figures from the U.S. Mint. The “I won’t buy an umbrella until it rains” crowd has been dumping gold while the case for ownership of safe haven gold has never been stronger.
The “I won’t buy an umbrella until it rains” crowd has been dumping gold while the case for ownership of safe haven gold has never been stronger.