You know the world is changing when the head of the world’s biggest bond fund recommends gold as his first asset choice.
You know the world is changing when the head of the world’s biggest bond fund recommends gold as his first asset choice.
In this week’s Barron’s Roundtable, Bond King Bill Gross affirms his bullish view on gold due to his assessment that central banks will continue to suppress interest rates by purchasing vast amounts of government debt with printed money. Gross notes that the financial system is now longer operating under free-market capitalism when the Fed is buying a “remarkable” 80% of debt issued by the U.S. Treasury. Massive deficits are being funded with printed currency on a global scale never attempted in the past and sooner or later, according to Bill Gross, inflation will blow past the central bank’s targeted rate of 2.5%.
The really big risk comes when huge holders of U.S. debt such as China and Japan become disgusted with U.S. fiscal and monetary policies and decide to dump their treasuries as inflation decimates the value of their holdings. Bill Gross tells Barron’s exactly what could go wrong and which gold investment he likes the best.
The big risk is that the Chinese would rather own something else. Investors can choose between artificially priced financial assets or real assets like oil and gold or, to be really safe, cash. The real risk to the financial markets is the marginal proclivity of investors to put their money in real assets, or under the mattress. Thus, my first recommendation is GLD — the SPDR Gold Trust exchange-traded fund. It has a fee, but it is an easy way for investors to buy a real asset.
Lots of things go into pricing gold, but real interest rates [adjusted for inflation] and expected inflation are two dominant considerations. Gold probably won’t move much from current levels unless real rates decline more or inflationary expectations rise from the current 2.5% to 3%, or higher. That’s what gets gold off the dime. It is a decent hedge. It doesn’t earn anything, but not much else earns anything either.
Pounding the table even harder than Gross, Fred Hickey, editor of the High-Tech Strategist, tells Barron’s that an explosive rally in gold seems imminent based on the massive bearish sentiment towards gold. Long term, Hickey sees gold hitting at least $5,000 per ounce, a target that Gold and Silver Blog also sees as a very reasonable future price target.
Hickey: I am recommending gold, as I have done for many years. I will continue to do so until the gold price hits the blow-off stage, which is nowhere in sight. I am excited about gold because sentiment is so negative. Gold could have a sharp rally at any time. The Hulbert Gold Newsletter Sentiment Index went deeply negative last week, indicating that gold-newsletter writers are recommending net short positions. When that happens, gold almost always rallies. The daily sentiment index for gold is at a 12-year low. Short positions by large speculators have doubled in the past few months. Sales of American Eagle coins hit a five-year low in 2012. Yet, the environment for gold couldn’t be better. We talked today about massive money-printing by all the major central banks. Real interest rates are negative. These are the best possible conditions for a gold rally.
Felix said gold could rally to the $1,800-an-ounce level, and I agree. If it breaks that, it will go to $2,000 or more. As long as we have unlimited quantitative easing, we have the potential for unlimited gains in the gold price. Gold could go to $5,000 or even $10,000. You can buy gold through the GLD or IAU, as we discussed. This year I recommend physical gold. You can buy American Eagle coins, or gold bars. Everyone should have some physical gold, and almost no one in the U.S. does.
Hickey also says that the price of gold is nowhere near a “blow off stage”, despite constant mainstream press reports of gold’s imminent collapse. For further discussion on this see The Gold Bubble Myth and Why There Is No Upside Limit For Gold and Silver Prices.


 By: Axel Merk
By: Axel Merk


 By:
By: With the United States rapidly approaching the debt ceiling limit, a dysfunctional and divided Congress appears unable to agree on either spending cuts or an increase in the debt ceiling. Absent some grand Congressional compromise, America’s nonstop trillion dollar deficit spending will rapidly push the nation to the brink of default before the end of next month.
With the United States rapidly approaching the debt ceiling limit, a dysfunctional and divided Congress appears unable to agree on either spending cuts or an increase in the debt ceiling. Absent some grand Congressional compromise, America’s nonstop trillion dollar deficit spending will rapidly push the nation to the brink of default before the end of next month.
 By: Axel Merk, Merk Investments
By: Axel Merk, Merk Investments 
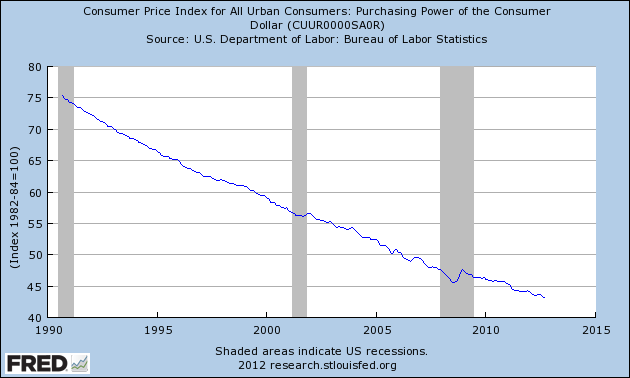
 Americans need to take a serious look at how the purchasing power of the dollar is being destroyed. Rampant poverty, declining real incomes and higher prices are all the guaranteed results of a Federal Reserve that remains committed to destroying the value of the dollar. A dollar saved today that has less purchasing power a year from now equates to the “silent” destruction of the dollar, an event which has gone virtually unnoticed and unprotested by the American public.
Americans need to take a serious look at how the purchasing power of the dollar is being destroyed. Rampant poverty, declining real incomes and higher prices are all the guaranteed results of a Federal Reserve that remains committed to destroying the value of the dollar. A dollar saved today that has less purchasing power a year from now equates to the “silent” destruction of the dollar, an event which has gone virtually unnoticed and unprotested by the American public.